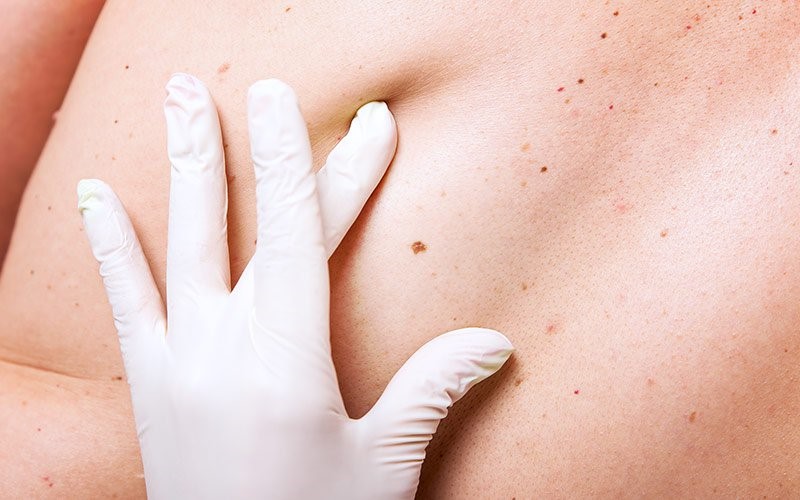
Full Skin Examination
A skin examination is a safe, non-invasive way to have a specialist or accredited expert in the field scan your skin for any suspicious looking moles are “ugly duckling” spots, and do a detailed dermoscopy examination of these spots to rule out cancer. Your doctor will take a complete skin history, including previous skin cancers, other skin conditions, and allergies before doing the skin exam. The exam typically involves lying on a sterile medical examination bed and changing position a few times to allow for a detailed scan of your skin. DermaSurg uses custom privacy screens to ensure your privacy while you disrobe to your undergarments.
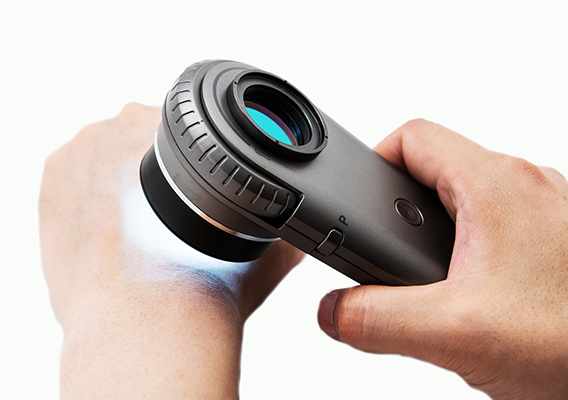

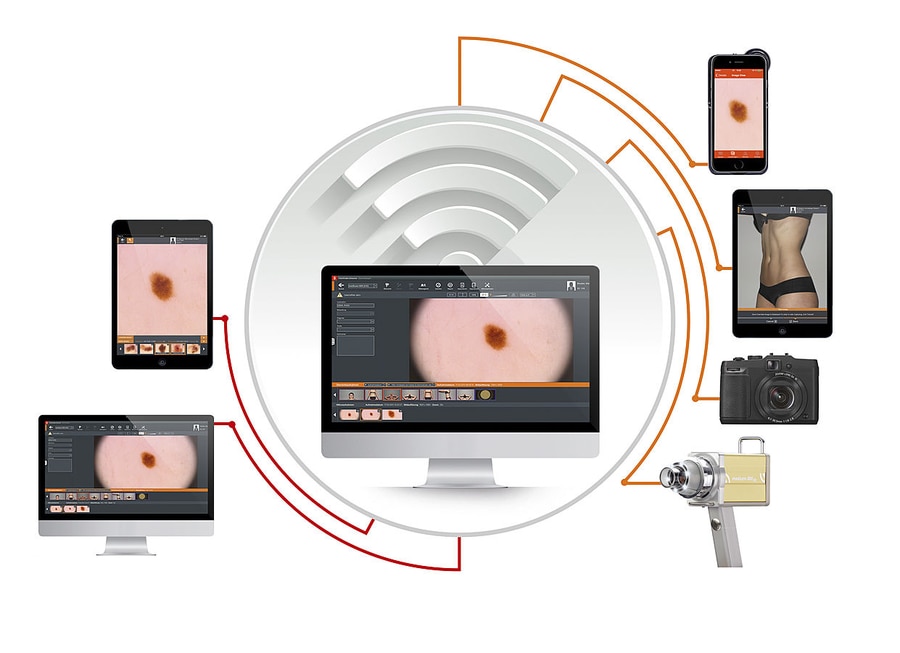
Dermoscopy (Dermatoscopy)
Expert use of dermoscopy has been shown to increase diagnostic accuracy for both melanocytic and non-melanocytic skin malignancies. The evidence for dermoscopy is such that it is now regarded as the standard of care for the evaluation of pigmented skin lesions. Dermoscopy is an advanced examination skill and accredited specialist training is required for effective use.
Our doctors have completed accredited training in the use of dermoscopy, and hold advanced certification in the field. They are Members of the International Dermoscopy Society.
Mole Mapping (Mole photography)
The risk of a long-term mole changing into a melanoma is extremely low (0.0005 – 0.003% **), so routine mole mapping of all moles is not helpful in a meaningful way. It certainly can be provided as an optional service, yet there is no Medicare rebate (Medicare concluded there is no convincing evidence that this technology saves lives). Yet not all “funny looking” coloured lesions need immediate biopsy or removal. Certain types are monitored at DermaSurg for a specified timeframe (usually around 3 – 6 months) using so-called “focused mole mapping” to monitor for changes that might identify those lesions that do require biopsy. People with extremely high individual risk of developing melanoma are also offered this service in combination with dermoscopy, which remains the gold standard examination to detect early melanoma.
** Tsao, et al. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139(3):282-288.
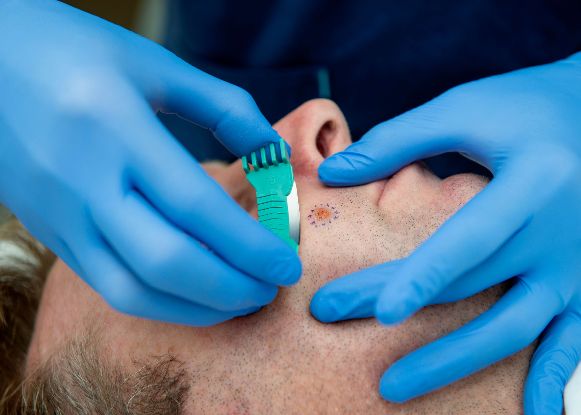
Skin Biopsy
A skin biopsy is one of the most important tools in the investigation and treatment of skin diseases and skin cancers. It involves the removal of a small piece of your skin for examination under a microscope by a specialist dermato-pathologist. The area is first cleaned and then a local anaesthetic is injected under the skin before the procedure is performed. There are several different types of skin biopsy including shave biopsy, punch biopsy, excisional biopsy, and deep shave removal biopsy. Most forms of biopsy require no sutures and heal spontaneously within a few days.
DermaSurg doctors normally perform shave biopsies for most type lesions and deep shave removal biopsies (saucerization) for pigmented (coloured) lesions as they heal fast and leave minimal scarring while providing good samples for pathologists to test. Occasionally an excision biopsy will be indicated and sutures inserted to optimize the healing process.
Skin Cancer Facts & Statistics
Non-melanoma skin cancers are far more common than melanoma, and make up over 85% of all skin cancer diagnoses. The two main types of non-melanoma skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
If you are diagnosed with a skin cancer you have a 50% increased risk of further skin cancers developing within 2 years. Skin cancers grow unpredictably, with some very quickly expanding or invading deeper layers, while others are very slow in getting bigger. It is best to get your skin cancer attended to as soon as possible. All skin cancers need to be removed, and most require some form of surgery. Most skin cancers treated appropriately and in a suitable time frame by an experienced skin surgeon will not recur or leave disfiguring scarring.
The larger the skin cancer, the bigger the excision needed to remove the cancer, the more scarring involved and the higher the cost of treatment. Medicare rebates are based on their size when removed.
While it is true that any doctor can cut out a skin cancer, not all possess the surgical skill needed to repair the surgical defect with the minimum amount of scarring and deformity. You will live a long time with the visible consequences of your decision, so please choose wisely.
You are not alone. By the age of 50, 1 in every 2 Australians have been diagnosed with a form of skin cancer. This increases to 2 in every 3 Australians by the age of 70.
The good news is that almost all forms of skin cancer is treatable and curable through relatively minor surgical or in some instances non-surgical treatments with a very high cure rate.
Non-melanoma (also called keratinocytic) skin cancers can be treated very effectively with chemotherapy, photodynamic therapy (PDT), or immunotherapy, or combination therapies when they are detected early. Read more about these modalities.
Our doctors are very experienced in surgery of the skin (dermasurgery) and have completed accredited training courses in skin cancer surgery during their postgraduate education. Read more about skin cancer surgery at DermaSurg.